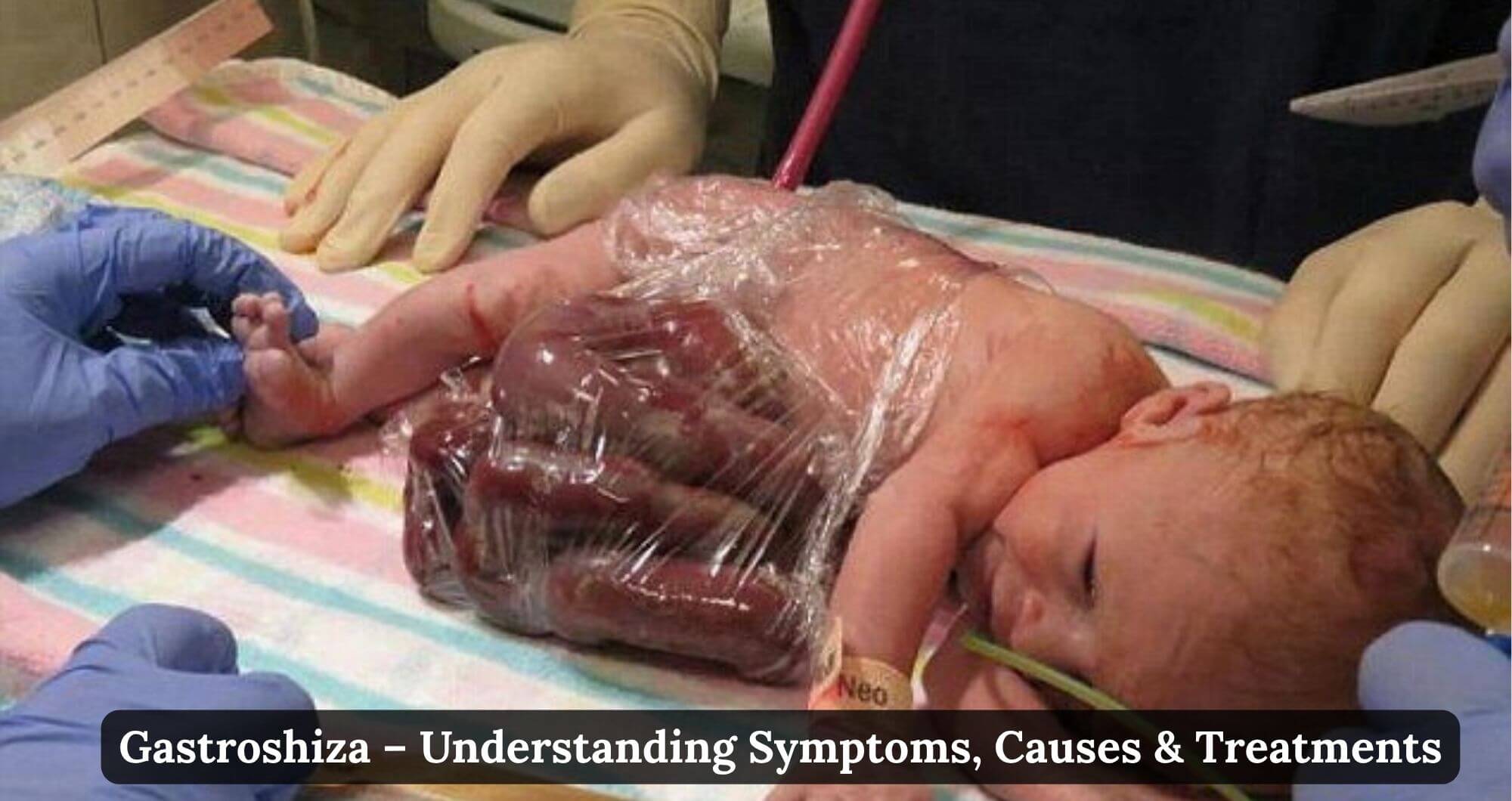
Gastroshiza may sound unfamiliar, but it’s a condition that impacts the lives of many. This congenital defect occurs when a baby is born with their intestines outside of their body, a situation that can be alarming for new parents and medical professionals alike. Understanding gastroshiza is crucial for anyone affected by it or looking to support those who are.
This article dives into the intricacies of gastroshiza, shedding light on its symptoms and causes while providing insights into effective treatment options. Here are helpful resources to help you manage this complicated condition, whether you’re looking for information for yourself or a loved one. Let’s explore how gastroshiza affects digestion and what steps can be taken to manage it effectively.
What is Gastroshiza and how it affects digestion
Gastroshiza involves the externalization of the intestines, which means that parts of the digestive tract are located outside the abdominal wall. This condition typically manifests in newborns, presenting a significant challenge at birth.
The exact mechanism behind gastroshiza is not fully understood, but it’s believed to arise from an early failure in the closure of the abdominal wall. As a result, infants with this condition often have their intestines exposed to amniotic fluid and other factors before birth.
Digestion in those affected by gastroshiza can be severely impacted due to several factors. The most immediate concern is ensuring that any exposed intestinal segments remain viable and functional. If these tissues become damaged or necrotic, further surgical interventions may be necessary.
Moreover, once treated surgically—typically involving repositioning the intestines inside the abdomen—infants may face ongoing challenges related to nutrient absorption and bowel function. Some children might experience feeding difficulties or require specialized diets as they grow older.
With proper medical care and monitoring after surgery, many individuals with gastroshiza can lead healthy lives; however, understanding how this condition affects digestion remains vital for managing long-term health outcomes effectively.
Common symptoms to recognize
Gastroshiza presents a range of symptoms that can significantly impact daily life. Abdominal discomfort is one of the most obvious symptoms, and it can vary in severity.
People who have gastroshiza also frequently feel bloating. Many report a sensation of fullness or swelling in the abdomen, which can lead to feelings of unease. This bloating might make it challenging to eat regular portions during meals.
In addition to these physical symptoms, changes in bowel habits are frequently observed. Individuals may experience diarrhea or constipation, contributing further to digestive distress. Tracking these patterns can help identify triggers related to diet or lifestyle choices.
Nausea is also prevalent among those affected by gastroshiza. It could occur independently or accompany other symptoms such as abdominal pain and bloating. Some people even experience episodes of vomiting when their condition flares up.
Fatigue is another key indicator that should not be overlooked. The combination of physical discomfort and nutritional deficiencies from malabsorption can leave individuals feeling excessively tired throughout the day. Recognizing these signs early on is crucial for seeking appropriate medical advice.
Causes and risk factors including diet and lifestyle
Gastroshiza is a condition that can be influenced by various causes and risk factors. For individuals impacted, it is essential to comprehend these factors. One of the primary risk factors includes genetic predisposition.
In order to control the symptoms of gastroshia, diet is crucial. High-fat, low-fiber diets can exacerbate digestive issues, leading to discomfort and complications. Consuming processed foods or excessive sugars might contribute to inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract.
Lifestyle choices also impact the severity of gastroshiza symptoms. A sedentary lifestyle often leads to poor digestion and weight gain, which can place additional strain on the digestive system. Incorporating regular physical activity helps maintain healthy bowel function.
Moreover, stress has been identified as another contributing factor. Chronic stress can disrupt normal digestive processes, potentially worsening gastroshiza symptoms over time. Mindful practices such as yoga or meditation may alleviate some stress-related impacts on digestion.
Certain medications could heighten risks associated with gastroshiza flare-ups. Medications affecting gut motility or altering gut flora should be used cautiously under medical guidance to avoid complications related to this condition.
Diagnosis methods and medical tests
Physicians typically ask about symptoms, onset, and duration to gather relevant information on the condition. This initial assessment helps identify any potential complications or associated issues.
After the preliminary evaluation, imaging tests often play a crucial role. An abdominal ultrasound is commonly used for infants suspected of having gastroshiza since it provides clear images of the abdominal organs and can detect abnormalities in real-time.
For more detailed insights, doctors may recommend X-rays or CT scans. These imaging techniques help visualize the extent of intestinal exposure outside the abdomen. They also assist in assessing any accompanying issues like bowel obstruction or other malformations.
In some cases, additional diagnostic tests may be necessary to rule out similar conditions. Blood tests can assess general health and look for indications of infection or nutritional deficits that might result from gastroshiza-related gastrointestinal issues.
Early diagnosis is key to effective treatment planning. Therefore, timely consultations with healthcare professionals are essential if symptoms suggestive of gastroshiza arise in newborns or during pregnancy screenings.
Treatment options: medications, diet, natural remedies
When it comes to treating gastroshiza, a combination of medications, dietary changes, and natural remedies can provide relief. Over-the-counter antacids may help alleviate discomfort from acid buildup. In more severe cases, prescription medications that reduce stomach acid production could be necessary.
Diet plays a crucial role in managing symptoms. Opting for smaller meals throughout the day rather than large ones can aid digestion significantly. Incorporating low-fat foods while avoiding spicy or acidic items helps minimize irritation in the digestive tract. High-fiber foods like whole grains and vegetables also support healthy digestion.
Natural remedies have gained popularity among those seeking alternative treatments for gastroshiza. Ginger tea is known for its soothing properties and can ease nausea associated with digestive issues. Peppermint tea may also help calm an upset stomach while promoting better bile flow.
Probiotics are beneficial as well; they replenish good bacteria in the gut, which may improve overall digestive health over time. Probiotic-rich foods include fermented vegetables like sauerkraut, kefir, and yogurt.
Always consult with healthcare professionals before starting any new treatment regimen to ensure it’s appropriate for your condition and needs.
Prevention tips and healthy habits
Preventing gastroshiza involves adopting a proactive approach to health and lifestyle choices. One of the most effective strategies is maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. These foods offer vital nutrients that promote the health of the digestive system.
Staying hydrated is crucial as well. Drinking adequate water daily helps keep your digestive system functioning smoothly. Constipation and other gastrointestinal problems brought on by dehydration might make gastroshiza symptoms worse.
Regular physical activity plays an important role too. Engaging in moderate exercise like walking or yoga can enhance digestion and help manage stress levels. Both factors are vital for supporting overall gut health.
Managing stress through mindfulness practices such as meditation or deep-breathing exercises can significantly benefit individuals at risk for gastroshiza. Stress often exacerbates digestive disorders, so finding ways to relax is essential.
Avoiding processed foods high in sugar and unhealthy fats can drastically improve your digestion. Limiting alcohol consumption also supports liver function while reducing potential irritants that could affect gastric stability over time. Prioritizing these habits fosters better long-term outcomes for those susceptible to gastroshiza.
Managing daily life with Gastroshiza

Living with gastroshiza can be challenging, but many strategies can aid in managing daily life. Understanding your condition is the first step. This awareness enables you to recognize triggers that exacerbate symptoms and make the required corrections.
Diet plays a crucial role in managing gastroshiza. Opt for smaller, more frequent meals rather than large portions to ease digestion. Drink plenty of water and include foods high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Keeping a meal journal could help you figure out what suits you best.
Physical activity is also beneficial. Gentle exercises such as walking or yoga can improve digestion and reduce stress levels. It’s essential to listen to your body; avoid any strenuous activities if they cause discomfort.
Mental health shouldn’t be overlooked either. Living with a chronic condition often brings emotional challenges like anxiety or depression. Consider mindfulness practices or seek support groups where sharing experiences can provide comfort and understanding.
Maintain open communication with healthcare providers about your symptoms and treatment plans. Regular check-ups ensure you’re on track and allow for adjustments when necessary, enhancing overall well-being while living with gastroshiza.
Conclusion and advice to consult healthcare professionals
Living with gastroshiza can be challenging. Understanding this condition is essential for managing symptoms effectively. Knowledge about the nature of gastroshiza helps individuals recognize when to seek help.
Consulting healthcare professionals is crucial at any stage of this journey. They can provide accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs. Their expertise ensures that you navigate the complexities of gastroshiza safely.
Regular check-ups are beneficial as they allow monitoring of your condition over time. Adjustments in treatment or lifestyle changes may be necessary based on progress. Healthcare providers can also address questions and concerns, providing reassurance along the way.
Moreover, connecting with specialists such as dietitians or nutritionists enhances management strategies. These experts offer insights into dietary adjustments that can alleviate discomfort, promoting a healthier lifestyle overall.
Don’t hesitate to reach out for support from community resources or online groups focused on gastroshiza awareness and education. Engaging with others who share similar experiences fosters understanding and encouragement throughout your health journey.
FAQs
Gastroshiza is a complex condition that can significantly impact daily life. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for anyone affected by this issue. Individuals experiencing signs of Gastroshiza should not hesitate to seek medical advice.
Now, let’s address some frequently asked questions about Gastroshiza:
What exactly is Gastroshiza?
A congenital condition known as gastroshiza occurs when the intestines protrude through a hole in the abdominal wall. The organs are not protected by a sac, in contrast to omphalocele, another syndrome that is comparable.
What are the common symptoms associated with Gastroshiza?
Common symptoms include visible intestinal loops outside the abdomen at birth, feeding difficulties, and potential complications like infection or problems with digestion.
What causes Gastroshiza?
The exact cause of Gastroshiza remains unclear. However, factors such as genetics and environmental influences during pregnancy play significant roles. A mother’s diet and lifestyle choices may also contribute to risk levels.
How is it diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically occurs prenatally via ultrasound or immediately after birth through physical examination. Imaging studies might be conducted postnatally to understand any complications better.
Are there effective treatments available for Gastroshiza?
Treatment usually involves surgical intervention shortly after birth to correct the defect. In addition to surgery, ongoing care may involve dietary adjustments and medications for managing digestive issues.
Can gastroesophageal reflux occur with this condition?
Yes, individuals with gastrointestinal defects like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) often have increased occurrences due to altered anatomy affecting digestion.
Is it possible to prevent gastroshiza from occurring?
While it’s challenging to prevent congenital conditions entirely since they are often genetic in nature; maintaining a healthy lifestyle during pregnancy—such as eating balanced meals and avoiding harmful substances—can reduce certain risks associated with developmental abnormalities.
How can someone manage life with Gastroshiza?
Managing life with Gastroshiza requires understanding your body’s needs and making informed health decisions every step of the way. Engaging healthcare professionals will provide valuable support throughout your journey.